Here we will find PID of process by CreateToolhelp32Snapshot() function.
Code
//hack.cpp
#include <windows.h> // 1
#include <stdio.h> // 2
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <tlhelp32.h> // 3
// find process ID by process name
int findMyProc(const char *procname) { // 4
HANDLE hSnapshot; // 5
PROCESSENTRY32 pe; // 6
int pid = 0; // 7
BOOL hResult; // 8
// snapshot of all processes in the system
hSnapshot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0); // 9
if (INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE == hSnapshot) return 0; // 10
// initializing size: needed for using Process32First
pe.dwSize = sizeof(PROCESSENTRY32); // 11
// info about first process encountered in a system snapshot
hResult = Process32First(hSnapshot, &pe); // 12
// retrieve information about the processes
// and exit if unsuccessful
while (hResult) { // 13
// if we find the process: return process ID
if (strcmp(procname, pe.szExeFile) == 0) { // 14
pid = pe.th32ProcessID; // 15
break; // 16
}
hResult = Process32Next(hSnapshot, &pe); // 17
}
// closes an open handle (CreateToolhelp32Snapshot)
CloseHandle(hSnapshot); // 18
return pid; // 19
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // 20
int pid = 0; // process ID // 21
pid = findMyProc(argv[1]); // 22
if (pid) { // 23
printf("PID = %d\n", pid);
}
return 0; // 24
}Explanation
- Includes the Windows API functions like CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(), Process32First(), etc.
- Provides standard I/O functions like printf().
- Adds support for process/thread/module enumeration APIs like PROCESSENTRY32, CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(), etc.
- Defines a function that takes a process name (
procname) and returns its PID. - Handle to the snapshot returned by CreateToolhelp32Snapshot().
- PROCESSENTRY32 structure to store process details.
- Initializes PID to 0 (i.e., “not found”).
- Stores result of process iteration of Step 13.
- Takes a snapshot of all running processes in the system.
- If Step 9 snapshot fails (invalid handle), then return 0 (indicating failure to find PID).
- Sets the size of the structure PROCESSENTRY32 (required before calling Process32First()).
- Retrieves info about the first process in the snapshot(captured in Step 9) using Process32First() function and store it in PROCESSENTRY32 structure.
- Loop through all processes in the snapshot got in Step 9.
- Compares current process name in PROCESSENTRY32 with the one provided (
procname) by user using strcmp() . - If matched, store its process ID in
pid. - Break the loop if process found.
- Move to the next process in the snapshot(captured in Step 9) using Process32Next() and store it in PROCESSENTRY32.
- Closes the snapshot handle to free resources using CloseHandle().
- Returns the founded PID (or 0 if not found) in Step 15.
- main() function accepting command-line arguments.
- Declares a variable
pidto store the process ID. - Calls
findMyProc()function created in Step 4 with the executable name passed viaargv[1]. - If a valid PID is found (non-zero) prints the PID with printf().
- If full program runs successfully return 0.
Compile and Run
Compile :
i686-w64-mingw32-g++ hack.cpp -o hack.exe -lws2_32 -s -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wno-write-strings -fno-exceptions -fmerge-all-constants -static-libstdc++ -static-libgcc -fpermissiveRun
- Move compiled
hack.exefrom Linux to Windows machine. - Run with
.\hack.exe <exe_name>command in PowerShell.
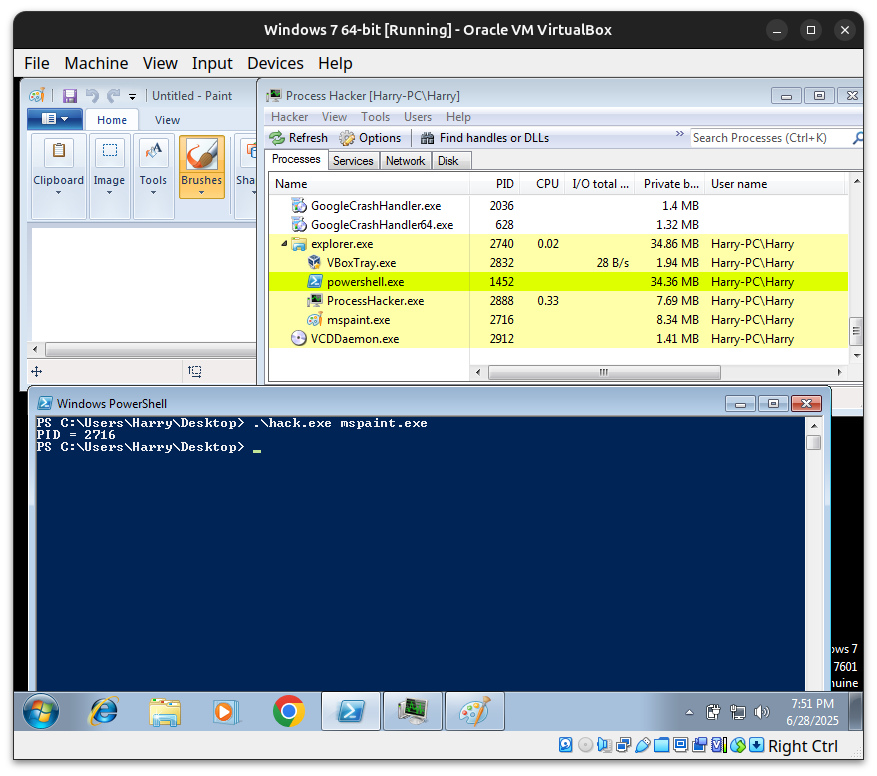
As we can see our code run successfully and we can verify founded PID with PID shown in Process Hacker.
